Rasa
Conversational AI platform for developers and enterprise teams to build text and voice assistants. Rasa provides an open-core engine, a no-code studio, and deployment options for self-hosted or managed environments designed for security, observability, and integration with existing systems.
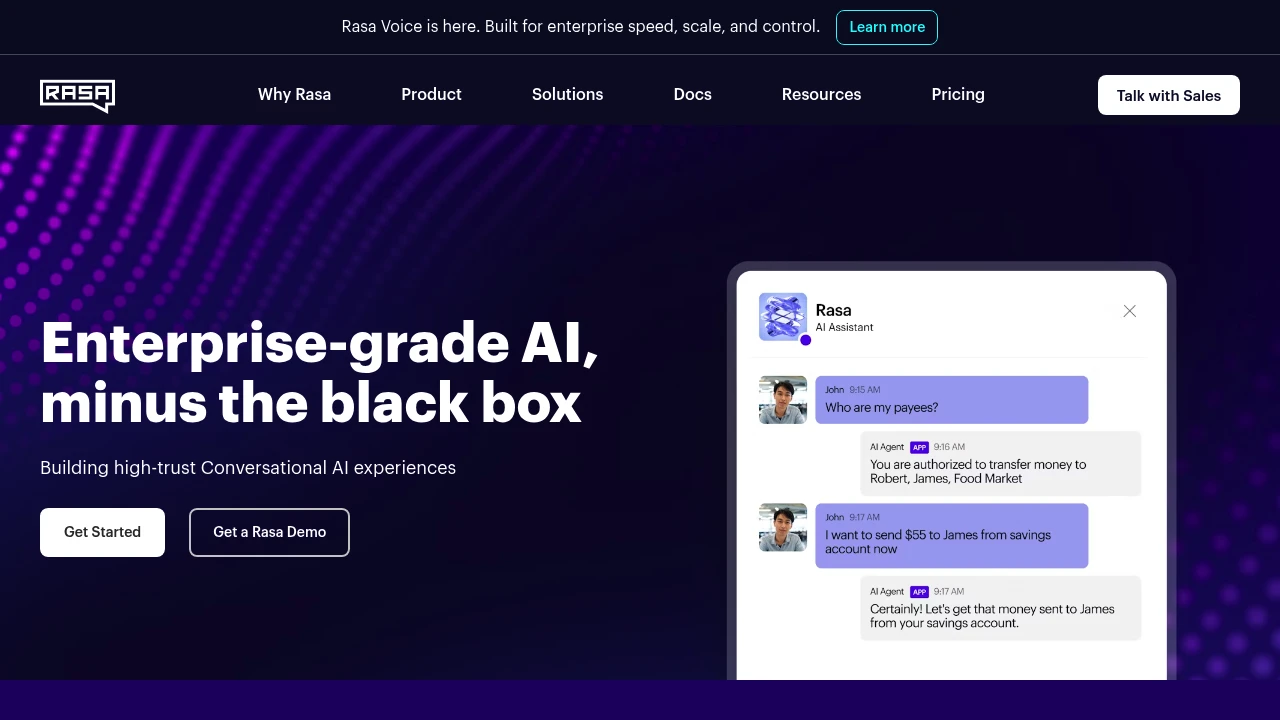
What is Rasa
Rasa is an open-core conversational AI platform used to build context-aware chatbots and voice assistants for enterprise and developer teams. The project contains a core machine learning engine for intent classification and dialogue management, tools for annotation and testing, and a separate UI for collaborative assistant development. Rasa is designed to be deployed where an organization needs it: self-hosted on private infrastructure or via a managed service offering.
Rasa emphasizes control over models, data, and integrations. That control is reflected in features for policy-driven dialogue flows, fine-grained customization of natural language understanding (NLU), and hooks for integrating business logic, back-end systems, and third-party language models. For teams that must meet compliance, data residency, or audit requirements, Rasa offers options that avoid sending production traffic to a third-party cloud NLP API unless explicitly configured to do so.
The platform targets a range of users: developers building custom conversational logic, conversational design teams that need iterative testing and review, and enterprise program owners who require governance, monitoring, and lifecycle management for assistants across channels.
Rasa is used in both greenfield projects and as a component inside larger contact center or customer engagement platforms. Many deployments combine Rasa's deterministic dialogue capabilities with external large language models (LLMs) for generative responses where appropriate, letting teams balance reliability and creativity.
Rasa features
What does Rasa do?
Rasa provides the building blocks to create, test, and operate conversational agents across text and voice channels. Key capabilities include intent classification and entity extraction (NLU), a dialogue management engine to track context and state, and action handling to call internal services or external APIs. These components can be extended with custom models or integrated with LLMs for generative output.
Beyond the core ML components, Rasa offers developer-focused tooling for training pipelines, versioning, and evaluation metrics, along with the collaborative UI known as Rasa Studio for conversation design and iteration. The platform supports automated testing, simulation of conversational flows, and interactive debugging tools to reproduce user sessions during development and after deployment.
For enterprise production needs, Rasa emphasizes scalability, observability, and security. Observability tooling includes logging, metrics, and tracing hooks so teams can monitor intent performance, fallback rates, and action execution. Security features and deployment patterns let organizations host Rasa inside their VPCs or behind corporate network controls to meet regulatory or internal policy requirements.
Rasa also includes components to connect assistants to channels such as web chat widgets, messaging platforms, and telephony systems. For voice use cases, Rasa can be integrated into voice stacks that handle ASR (automatic speech recognition) and TTS (text-to-speech), allowing the conversational engine to focus on intent and dialogue state while external voice services handle audio input/output.
Rasa pricing
Rasa offers flexible pricing tailored to different business needs, from individual developers using the open-source core to enterprise customers requiring managed hosting, advanced security, and dedicated support. Pricing typically reflects deployment choices (self-hosted vs managed), the number of assistants or virtual agents, and enterprise add-ons such as SLAs, onboarding, and dedicated engineering support. Check Rasa's current pricing options for public plans and enterprise engagement models.
Typical Rasa purchasing patterns include:
- Free Plan: The open-source Rasa framework and community editions can be used at no licensing cost for development and self-hosted production. This is commonly chosen by developers and small teams for proof-of-concept work.
- Starter: Paid packages for small teams that want hosted components, basic support, and easier onboarding; pricing is usually monthly or annual with per-assistant or seat-based metrics.
- Professional: Mid-market packages that include extended support, observability tooling, and integration assistance; these plans commonly add SLAs and feature parity with enterprise needs.
- Enterprise: Custom contracts for large organizations that require on-premise deployment options, single sign-on, compliance certifications, dedicated support, and professional services.
The final cost for enterprise deployments often depends on expected throughput, concurrency, and support levels. Many customers negotiate yearly contracts that include implementation, training, and success management. Visit their official pricing page for the most current information.
How much is Rasa per month
Rasa offers flexible monthly plans and also supports annual commitments with discounts. For many teams, monthly SaaS-style billing applies to hosted or managed offerings and starts at levels appropriate for small teams but scales to high-volume enterprise tiers. If you prefer self-hosting, there may be no per-month license fee for the open-source core, though operational costs for infrastructure and support should be accounted for.
For exact monthly rates on managed offerings, consult Rasa's published pricing or contact sales for a quote. Check Rasa's current pricing options to compare monthly and enterprise billing models.
How much is Rasa per year
Rasa offers annual billing options that commonly include discounts versus month-to-month agreements and may bundle onboarding, training, and support hours. Enterprise contracts are typically negotiated on an annual basis and can include professional services, feature customization, and multi-year discounts depending on scope.
Organizations running the open-source core on their infrastructure pay operational costs (hosting, monitoring, maintenance) annually, which vary by cloud provider and traffic. For detailed annual pricing and saved percentage for prepaying yearly, review Rasa's pricing and plans or contact their sales team.
How much is Rasa in general
Rasa pricing ranges from free (open-source core) to custom enterprise contracts that can reach tens of thousands of dollars per year for large-scale deployments. Small teams can often get started with the free self-hosted stack at minimal software cost, while larger companies budget for managed services, compliance, and dedicated support that increase total cost of ownership.
When planning costs, include hosting and infrastructure, monitoring, developer and conversational design labor, and any third-party services for speech, analytics, or LLM access. For most enterprises the software licensing portion is one component of a multi-part budget. Visit their official pricing page for the most current information.
What is Rasa used for
Rasa is used to build conversational assistants that automate customer service, handle transactional workflows, assist employees with internal processes, and serve as the conversational layer in omnichannel contact centers. Common use cases include FAQ automation, order status lookups, appointment scheduling, authentication flows, and guided troubleshooting.
Because the platform supports both text and voice, Rasa is suitable for web chatbots, mobile app assistants, messaging integrations (SMS, WhatsApp), and voice IVR systems. Teams often combine Rasa with CRM and ticketing systems so bots can read or update customer records and escalate to human agents as needed.
Enterprises use Rasa to centralize conversational logic and enforce business rules, ensuring interactions follow compliance requirements and maintain consistent brand voice. Rasa’s extensibility allows organizations to integrate custom back-end connectors, embedding fine-grained control over when to invoke LLMs, when to use deterministic responses, and how to log interactions for auditability.
Operationally, Rasa helps reduce repetitive agent work by increasing containment rates, shortening time-to-resolution on common issues, and enabling 24/7 automated handling of routine requests. At the same time, it provides tools for monitoring performance so teams can iterate models, adjust NLU training, and update business logic based on real user conversations.
Pros and cons of Rasa
Pros:
- Strong control and data privacy: Rasa can be self-hosted behind corporate firewalls, which helps meet data residency and compliance requirements.
- Developer-first and extensible: The platform allows custom NLU pipelines, dialogue policies, and integrations with existing systems and LLMs.
- Open-core and community momentum: The open-source project provides a low-cost entry point and an active community for best practices and shared tooling.
- Enterprise features for observability and governance: Managed offerings and enterprise modules add monitoring, role-based access, and professional support.
Cons:
- Higher implementation effort: Building production-ready assistants often requires engineering resources for integration, testing, and ongoing maintenance compared with some turnkey SaaS bots.
- Operational overhead for self-hosting: Teams choosing the open-source route are responsible for infrastructure, scaling, and uptime.
- Learning curve for non-technical users: Although Rasa Studio offers no-code flows, the most advanced capabilities still rely on developer involvement.
Choosing Rasa is often a trade-off between control and time-to-deploy. Organizations that prioritize data control, custom logic, and the ability to mix deterministic and generative strategies will find Rasa well-suited, while teams seeking a plug-and-play conversational SaaS with minimal engineering may consider other hosted providers.
Rasa free trial
Rasa’s open-source core can be used without a licensing fee, which effectively serves as a perpetual trial for developers. For managed or enterprise features, Rasa typically offers trial engagements or proof-of-concept projects tailored to a customer’s needs—these trials allow teams to validate the platform’s fit with their data flows and compliance constraints before committing to a contract.
If you want to evaluate Rasa in a production-like setup, plan a short proof-of-concept that includes representative traffic, integration with key back-end systems, and acceptance criteria such as containment rate improvement or reduction in escalation to human agents. Use these trials to measure metrics like intent accuracy, fallback rates, and overall user satisfaction.
For enterprise pilots, engage Rasa’s sales or solutions engineering team to obtain trial access to managed components, performance baselines, and a scoped implementation plan. Check Rasa’s documentation and resources for guidance on setting up reproducible evaluation environments.
Is Rasa free
Yes, Rasa provides an open-source core that can be used at no license cost. The Rasa Open Source project includes the NLU and Core libraries needed to build and run conversational assistants. Organizations choosing commercial or managed features pay for additional hosting, support, or enterprise-level functionality.
Rasa API
Rasa exposes APIs for both real-time conversation handling and management operations. The REST and socket APIs allow channels and front-end clients to send user messages and receive bot responses, while administrative endpoints support model training, model swapping, and telemetry retrieval. This API-based approach is designed to integrate with existing messaging platforms, telephony connectors, and orchestration layers.
In addition to runtime APIs, Rasa provides programmatic interfaces for data import/export, NLU training data management, and evaluation metrics, enabling automation of CI/CD pipelines for conversational models. For voice or telephony deployments, teams typically combine Rasa’s dialogue APIs with an ASR/TTS stack and a session manager to maintain end-to-end audio lifecycle.
Developers should consult Rasa’s official API documentation for versioned endpoint definitions, authentication mechanisms, and best practices for scaling and securing production traffic: check the Rasa docs. The documentation describes SDK hooks, action server patterns, and recommended deployment topologies for high-availability production systems.
10 Rasa alternatives
Paid alternatives to Rasa
- Dialogflow — Google Cloud’s conversational platform that provides NLU, pre-built agents, and straightforward integration with Google Cloud services; good for rapid prototyping with managed hosting.
- IBM Watson Assistant — Enterprise-grade assistant platform that includes dialog modeling, integration with IBM Cloud, and advanced enterprise security options.
- Amazon Lex — AWS service that powers conversational interfaces using the same technologies behind Alexa; tightly integrated with AWS services for scalability.
- Microsoft Bot Framework — Component-based framework with Azure Bot Service for building and connecting bots across Microsoft Teams, web chat, and other channels.
- LivePerson — Focused on conversational commerce and enterprise messaging, LivePerson combines conversational AI with agent handoff and analytics.
- Ada — A no-code customer service automation platform that emphasizes business-user configurability and quick time-to-value for support automation.
- Zendesk Answer Bot — Built for customer support workflows and integrated into the Zendesk suite for ticket deflection and help center automation.
Open source alternatives to Rasa
- Botpress — Modular, on-premise chatbot framework with a visual flow builder and extensible modules; suitable for teams that want a developer-friendly open-source alternative.
- DeepPavlov — Open-source library of conversational components and pre-trained models, commonly used in research and custom NLU pipelines.
- ChatterBot — Python library for building simple conversational agents with machine learning-based response selection; useful for prototyping and educational projects.
- OpenDialog — Conversation design platform focused on declarative conversation modeling and business-rule-driven dialogues.
- Mycroft — Open-source voice assistant stack that can be combined with other NLU engines for voice-first deployments.
Frequently asked questions about Rasa
What is Rasa used for?
Rasa is used for building conversational assistants and chatbots for text and voice channels. Organizations use Rasa to automate customer interactions, support workflows, and internal employee assistants while retaining control over data, integration, and custom business logic. It supports on-premise and cloud deployment patterns so teams can select the operational model that meets compliance and performance needs.
How does Rasa handle integrations with enterprise systems?
Rasa provides APIs and action hooks for integrating with backend systems and CRMs. Developers implement custom actions that call internal services, databases, or third-party APIs; these actions run in an action server that can be secured within the organization’s network. Rasa’s extensibility patterns let teams pipeline contextual data into conversations and perform side effects like ticket creation or data lookups.
Does Rasa support voice assistants?
Yes, Rasa supports voice use cases when combined with ASR and TTS components. Rasa focuses on the conversational logic and state management, while audio capture and playback are handled by speech services. This separation allows teams to use preferred speech providers and connect them to Rasa’s dialogue APIs for full voice assistant implementations.
Can Rasa use large language models (LLMs)?
Yes, Rasa can be integrated with LLMs for generative responses. Teams commonly use hybrid approaches that combine Rasa’s deterministic dialogue handling with LLMs for natural responses, summarization, or context enrichment. Integration patterns let organizations gate, filter, or constrain LLM outputs to enforce business rules and safety.
Is Rasa secure for enterprise deployments?
Yes, Rasa supports enterprise deployment patterns that prioritize security and compliance. The platform can be self-hosted behind corporate firewalls, integrated with single sign-on (SSO), and configured to meet data residency requirements. For formal compliance claims, consult Rasa’s security documentation and engage their enterprise team for certification details and architecture guidance.
Why would a company choose Rasa over a fully managed SaaS bot?
Companies choose Rasa when they need control over data, custom business logic, and flexible deployment. Rasa’s open-core approach avoids vendor lock-in and allows teams to host models and logs in their environment. This control is important for regulated industries or organizations with complex back-end integrations and strict audit requirements.
When should an organization start with Rasa Open Source versus a managed plan?
Start with Rasa Open Source for experimentation and proofs-of-concept if you have developer resources. If you need production SLAs, dedicated support, or faster time-to-value with reduced operational overhead, consider a managed or enterprise plan. The choice depends on required uptime, compliance obligations, and internal operational capacity.
Where can I find Rasa documentation and learning resources?
Rasa maintains comprehensive documentation and community resources on their site. Developers and conversational designers can access guides, tutorials, and API references at Rasa’s official docs hub; the community forum and GitHub repository provide examples and community-contributed components. See Rasa’s documentation and tutorials for step-by-step instructions.
How much does Rasa cost for enterprise use?
Rasa offers flexible pricing plans tailored to different organization sizes and deployment choices, ranging from the free open-source core to negotiated enterprise agreements that include managed services and support. For specific quotes and billing options, check Rasa’s current pricing options and contact their sales team for an enterprise proposal. Visit their official pricing page for the most current information.
Does Rasa offer partner programs or an affiliate option?
Rasa works with systems integrators, partners, and consultancies for implementation services. While typical partner engagement involves certified consultants and professional services firms, organizations interested in referral or reseller arrangements should contact Rasa’s business development or partner team to learn about partner tiers and requirements.
rasa careers
Rasa maintains engineering, product, and customer-facing roles focused on conversational AI and open-source development. Positions typically include software engineering, machine learning research, developer advocacy, and solutions engineering. For up-to-date job listings and hiring practices, visit Rasa’s careers portal and LinkedIn page where the company posts openings and details about culture and benefits.
rasa affiliate
Rasa engages with partners and consultants who build on the platform; formal affiliate-like referral models vary by region and partner type. Organizations interested in referral or partnership opportunities should inquire through Rasa’s partner or sales contact channels to learn about current programs, certification tracks, and commercial terms.
Where to find rasa reviews
You can find independent reviews and case studies for Rasa on technology review sites, analyst reports, and Rasa’s customer success pages. For firsthand user feedback, check community forums, GitHub discussions, and case studies published by Rasa customers such as T-Mobile and Lemonade that describe implementation outcomes and business impact. Rasa’s site also hosts customer stories and technical deep dives for real-world examples.